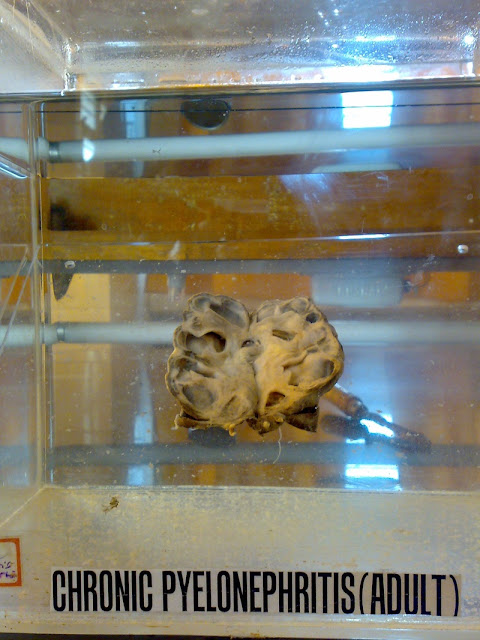
Osteosarcoma is the most common bone cancer in children and adolescents, and the third most common cancer in adolescence.
Osteosarcoma is most common between the ages of 10 and 25 when the bones are rapidly growing
Risk factors :
- Exact cause is unknown associated with random genetic mutations of osteoblasts
- Transmission of diseases including retinoblastoma, Li Fraumeni syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome,- Paget's disease, and Werner's syndrome from parents to offspring
- Only known environmental risk factor is exposure to radiation
Symptoms include :
- Bone fracture (may occur after what seems like a routine movement)
- Bone pain
- Limitation of motion
- Limping (if the tumor is in the leg)
- Pain when lifting (if the tumor is in the arm)
- Tenderness, swelling, or redness at the site of the tumor
Investigations :
- Biopsy (at time of surgery for diagnosis)
- Blood tests
- Bone scan to see if the cancer has spread to other bones
- CT scan of the chest to see if the cancer has spread to the lungs
- CT scan and MRI scan
- PET scan
- X-ray
Diagnosis :
- Chemotherapy is the first line of treatment, drugs include
Carboplatin (Paraplatin), Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), Doxorubicin (Adriamycin), Epirubicin, Etoposide, Ifosfamide (Ifex), Methotrexate (high dose) with leucovorin
- Surgery is used after chemotherapy to remove any remaining tumor. In most cases, surgery can remove the tumor while saving the affected limb (this is called limb-salvage surgery)
Prognosis :
If the tumor has not spread to the lungs (pulmonary metastasis), long-term survival rates are better
Osteosarcoma is most common between the ages of 10 and 25 when the bones are rapidly growing
Risk factors :
- Exact cause is unknown associated with random genetic mutations of osteoblasts
- Transmission of diseases including retinoblastoma, Li Fraumeni syndrome, Rothmund-Thomson syndrome,- Paget's disease, and Werner's syndrome from parents to offspring
- Only known environmental risk factor is exposure to radiation
Symptoms include :
- Bone fracture (may occur after what seems like a routine movement)
- Bone pain
- Limitation of motion
- Limping (if the tumor is in the leg)
- Pain when lifting (if the tumor is in the arm)
- Tenderness, swelling, or redness at the site of the tumor
Investigations :
- Biopsy (at time of surgery for diagnosis)
- Blood tests
- Bone scan to see if the cancer has spread to other bones
- CT scan of the chest to see if the cancer has spread to the lungs
- CT scan and MRI scan
- PET scan
- X-ray
Diagnosis :
- Chemotherapy is the first line of treatment, drugs include
Carboplatin (Paraplatin), Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), Doxorubicin (Adriamycin), Epirubicin, Etoposide, Ifosfamide (Ifex), Methotrexate (high dose) with leucovorin
- Surgery is used after chemotherapy to remove any remaining tumor. In most cases, surgery can remove the tumor while saving the affected limb (this is called limb-salvage surgery)
Prognosis :
If the tumor has not spread to the lungs (pulmonary metastasis), long-term survival rates are better

![Validate my Atom 1.0 feed [Valid Atom 1.0]](valid-atom.png)